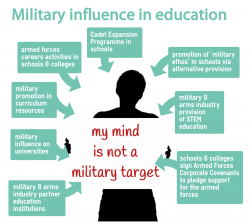
 The UK armed forces visit thousands of schools each year. They offer career presentations, curriculum resources and other activities aimed at promoting the interests of the military and long-term recruitment. Since 2012, the Department for Education have promoted ‘military ethos’ programmes such as cadet units in state schools and ‘alternative provision with a military ethos’.
The UK armed forces visit thousands of schools each year. They offer career presentations, curriculum resources and other activities aimed at promoting the interests of the military and long-term recruitment. Since 2012, the Department for Education have promoted ‘military ethos’ programmes such as cadet units in state schools and ‘alternative provision with a military ethos’.
The armed forces and arms companies are increasingly involved in the provision of STEM (science, technology, engineering and maths) activities for school and college students. and they also sponsor a number of careers-led secondary schools. The armed forces also now sponsor youth organisations like Girlguiding and Scouts. See more here.
Should the armed forces by given access to children within education? How can we challenge their activities in schools and colleges? How can a more balanced view of the military be given to young people?
While there are claims that school involvement is not about recruiting young people, the Ministry of Defence has itself stated that visits to educational establishments are a ‘powerful tool for facilitating recruitment’.
In having contact with young people, the military aim to sow seeds in impressionable young minds. In 2007, the head of the Army’s recruitment strategy said, “Our new model is about raising awareness, and that takes a ten-year span. It starts with a seven-year-old boy seeing a parachutist at an air show and thinking, ‘That looks great.’ From then the army is trying to build interest by drip, drip, drip.”
The influence of military interests in education and youth activities raises concerns around:
- recruiting-related activities in school
- child welfare issues
- the unrepresentative portrayal of the armed forces
- weapons in schools and at public events aimed at interesting children and teenagers in a military career
- the need for balance in teaching controversial issues
- the lack of balance with other career providers coming into schools
- the lack of parental consultation and policy scrutiny
- concerns around targeting disadvantaged areas and prioritising over other youth activities
- lack of balance with education for peace
- marginalising individuals and groups to do not wish to participate in military-related activities
See our briefing on Military involvement in education and youth activities in the UK.
We recognise the importance of debate and critical thinking in helping young people make an informed choice about the military and its activities. This is particularly important for those thinking of a career in the forces, a uniquely risk-laden occupation. If the military are allowed to have a presence and influence in the UK education system then it should be balanced by a thorough exploration of opposing views and approaches, as demanded by the 1996 Education Act.
Useful resources
Camouflage Kids: How the military affects young people’s lives
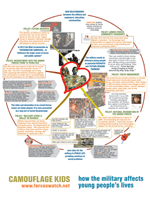 A ForcesWatch poster showing policy, cultural and other recent developments affecting the extent of military influence in young people's lives.
A ForcesWatch poster showing policy, cultural and other recent developments affecting the extent of military influence in young people's lives.
The military’s influence in UK education
 by Emma Sangster in Sowing Seeds: The Militarisation of Youth and How to Counter It, War Resisters International, 2013
by Emma Sangster in Sowing Seeds: The Militarisation of Youth and How to Counter It, War Resisters International, 2013
‘Catch them young before the army loses them’
 by David Gee in Sowing Seeds: The Militarisation of Youth and How to Counter It, War Resisters International, 2013
by David Gee in Sowing Seeds: The Militarisation of Youth and How to Counter It, War Resisters International, 2013
Unpacking ‘recruitment’: what does the MoD mean when it says the armed forces do not run recruitment activities in schools?
ForcesWatch briefing: Expanding the Cadets and ‘military ethos’ in UK schools
 A ForcesWatch briefing on the Government policy of expanding cadets and promoting 'military skills and ethos' in schools.
A ForcesWatch briefing on the Government policy of expanding cadets and promoting 'military skills and ethos' in schools.